Audi has been piloting an AI tool that analyses information about suppliers to assess their sustainability in terms of environmental pollution, human rights and corruption. It also monitors information about potential cyber-crimes.
The project has been running since October 2020 and Audi is using intelligent algorithms to analyse news about suppliers from publicly available online media sources and social networks across 150 countries. The system alerts Audi to any potential violations of its sustainable criteria.
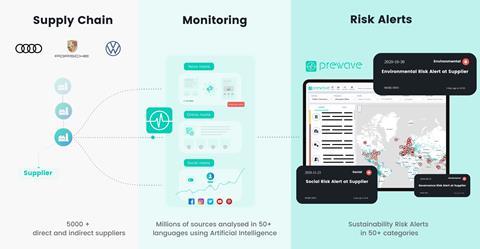
With the information Audi can demand a supplier partner immediately initiate improvements or it can terminate the business relationship.
“Artificial intelligence and machine learning are becoming enablers of sustainability at our company,” said Dirk Große-Loheide, who is responsible for procurement and IT at Audi.
AI start-up Prewave has developed the tool, which uses automotive speech recognition in 50 languages to check for potential violations of Audi’s sustainability criteria and alerts the carmaker to them. The algorithms are constantly learning and therefore the system is increasing its ability to recognise developing risks, according to the company.
The VW and Porsche brands are also reported to be testing the technology.
“We are delighted to be working with Audi, Volkswagen, and Porsche to carry out this flagship project in the automotive industry,” said Harald Nitschinger, CEO of Prewave. ”Our technology is being used to screen thousands of globally distributed suppliers for sustainability risks in real time. Machine learning and automated language processing thus makes possible what would be impossible to do manually – perform continuous risk assessments across the entire supply chain that Procurement can then use to proactively approach suppliers.”
The tool monitors a wide range of categories related to social and environmental issues. In social it looks for violations of labour law, unrest in the workforce, child labour, or discrimination in the workplace. In terms of environmental issue the algorithm draws on public data regarding, air and water pollution, water consumption or waste problems, among other issues. The AI also analyses reports indicative of suspected cyber-attacks, data fraud or data theft.
“Analysing massive amounts of data using artificial intelligence highlights how digitalisation can uncover risks in our supply chain,” said Susanne Lenz, supply chain sustainability strategist at Audi. “Thanks to our collaboration with Prewave, we are using an adaptive, powerful tool to increase transparency and efficiently monitor sustainability agreements.”
Code of conduct
Audi has outlined its sustainability requirements for suppliers in its Code of Conduct for Business Partners, which provides guidelines for environmental and social conduct. The guidelines are a part of the carmaker’s risk assessment process. A sustainability rating (S rating) for suppliers has been a mandatory criterion for awarding contracts since 2019 and Audi only works with companies that pass the audit.
Audi said that in 2020 more than 13,000 suppliers provided the wider VW Group with a self-assessment of their own sustainability performance. More than 800 suppliers were audited on site, and more than 1,300 have improved their sustainability performance and now meet Audi’s standards.
Audi has more than 14,000 direct suppliers from around 60 countries and they are expected to ensure that their upstream partners comply with the sustainability requirements laid out in the Code of Conduct for Business Partners.



























No comments yet